While we sometimes find compelling investment opportunities in obscure corners of the market, we also discover them by looking closely at something that is an integral part of our everyday lives.
Such is the case with the global digital payments industry, the multifaceted and complex financial transaction ecosystem that allows individuals around the world to pay for goods and services without using cash.
One thing that makes digital payments particularly compelling for fundamental managers focused on finding sustainable sources of value creation is that it represents a truly enormous addressable market that continues to expand due to strong, durable secular tailwinds.
Many analysts estimate global business-to-consumer (B2C) digital payments volumes to be more than $30 trillion.
Trends driving the growth of this market are numerous, and are even more important as individuals further embrace all things digital in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Below we discuss five: a shift away from cash, the growth of e-commerce, usage by small and midsize businesses (SMBs), underpenetration in international markets, and government support.
The global shift away from using cash is a rising tide that is lifting all boats within the payments industry.
1. A Shift Away from Cash
The global shift away from using cash is a rising tide that is lifting all boats within the payments industry. From 2012 to 2017, the volume of global payments using credit or debit cards (which represent the vast majority of digital, or noncash, payments) grew at a 6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), and the percentage of transactions conducted via cards increased from about 34% in 2012 to 42% in 2017.[1]
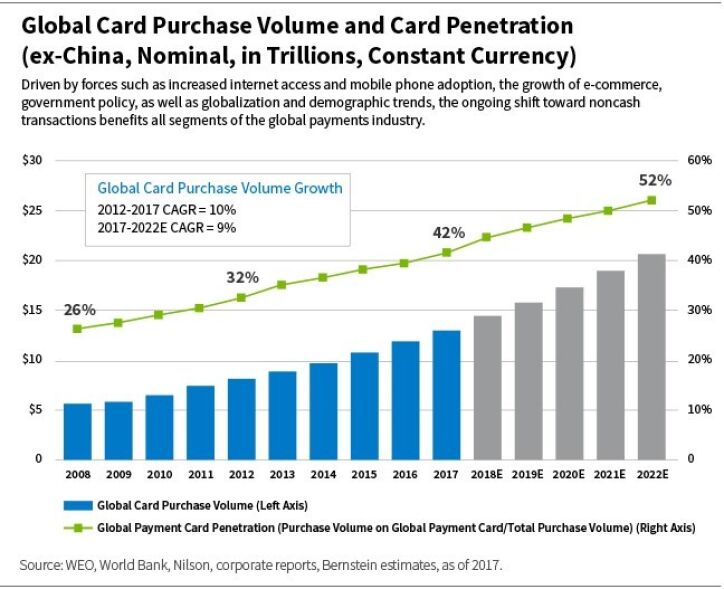
In addition to the expansion of e-commerce and increased internet access in emerging markets, digital payments volume growth is also supported by in-store retail purchases that increasingly rely on cards and “digital wallets.”
Other secular trends supporting the growth in digital payments include the penetration of mobile phones globally; a younger, more tech-focused consumer population; online gaming with in-app purchases; growth in domestic and global travel; ridesharing services (as well as pay-per-minute scooters and motorized bicycles); and peer-to-peer payment systems (e.g., Venmo).
2. Growth of E-commerce
E-commerce is driving digital payments volume growth in two ways: consumers make more purchases because of the convenience of buying online or via mobile apps, and, relative to in-store purchases, a significantly higher percentage of e-commerce transactions is completed using a credit or debit card.
While e-commerce benefits all segments of the payments industry, it is especially important for merchant acquirers, which are the entities that enable merchants to accept credit cards and other forms of digital payments.
We will discuss merchant acquirers in great detail later in this series, but for now, suffice it to say that when evaluating merchant acquirers, we pay close attention to a company's exposure to e-commerce, as we believe that it represents one of the most powerful and durable growth drivers in digital payment volumes.
3. Usage by SMBs
In addition to the growing volume of transactions, merchant acquirers can drive revenue by providing higher-margin, value-added services. These opportunities are especially prevalent when serving SMBs.
We discuss SMBs more later in this series, but for now, just understand that merchant acquirers can bundle ancillary services—such as inventory management software, working capital loans, faster payment receipts, targeted marketing, and loyalty programs—into systems designed to meet the needs of SMBs.
4. Underpenetration in International Markets
Digital payments penetration in most international markets trails the levels seen in the United States. This is especially true in emerging markets, providing significant room for volume growth as countries such as India shift to a digital economy.
5. Government Support
By and large, governments are supportive of the transition to digital payments because it improves tax collection and reduces the size of the black market economy that depends on cash. Furthermore, governments support efforts to extend banking services to under- or unbanked populations.
Global Industry, Regional Trends
These factors explain why the digital payments industry represents a truly enormous addressable market that continues to expand due to strong, durable secular tailwinds.
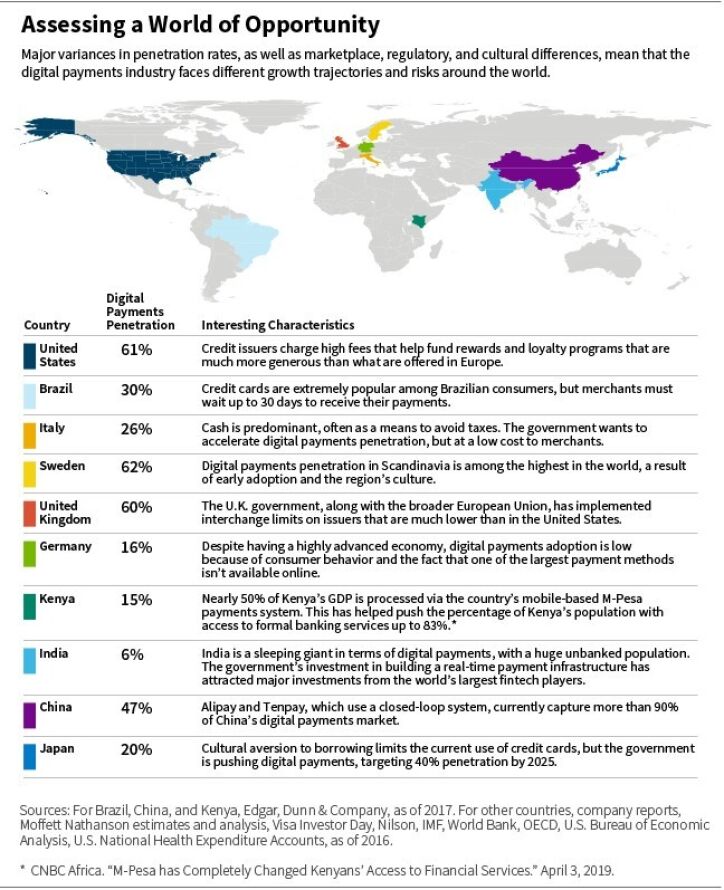
But the industry is also compelling because penetration varies significantly across regions and countries, creating opportunities for fundamental managers to find value.
For example, the United States is a more mature market with high penetration levels, while usage in Europe varies drastically by country. In emerging markets, penetration is typically low, providing a long runway for growth.
Country-specific differences, shown below, provide insights into the nature of various opportunities around the world.
Up Next
Disruption is always a consideration when analyzing an industry, and this threat varies significantly across the segments of the digital payments industry. But there is nothing overpriced or inefficient about the current system that would make it ripe for disruption. In our next post, we explain why.
Digital Payments Series
Part 1: Why We Find Digital Payments Compelling
Part 3: Disruption and Growth in Digital Payments
Part 4: Follow the Money in Digital Payments
Part 5: More Competition for Merchant Acquirers
Part 6: Digital Payments Issuers Face Regulatory Risk
Part 7: Networks: The Rails That Connect Digital Payments
Global Research Analysts Drew Buckley, CFA, and Kwesi Smith, CFA, contributed to this blog post.
Daniel Hill, CFA, is a research analyst on William Blair's Global Equity team.
Tipp: Dieser Beitrag ist auch im "Investment Insights"-Blog von William Blair verfügbar.
William Blair Updates per E-Mail erhalten
[1] WEO, World Bank, Nilson, corporate reports, and Bernstein estimates.
Weitere beliebte Meldungen:





